Multi-Bot Architecture: Revolutionizing Automation Across Industries
In today’s digital transformation, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has become a pivotal technology, enabling organizations to automate mundane and repetitive tasks. As Enterprises scale and the complexity of processes increases, and enterprise business applications support scaling and business needs. In this environment a single bot approach is often insufficient to handle the complexity and workload. This is where Multi-Bot Architecture can be a game-changer, offering scalability, efficiency, performance and resilience. In this document we elaborate on Multi-Bot Architecture, supported by some real-world use cases, advanced concepts and best practices.
What is Multi-Bot Architecture?
Multi-Bot Architecture refers to a distributed network of bots working collaboratively to automate large and complex processes. Rather than relying on a single bot, organizations deploy multiple bots that function simultaneously, either working on the same process (dividing the workload) or on different processes altogether. These bots are managed centrally via an Orchestrator, ensuring balanced distribution of work and smooth execution.
Why Multi-Bot Architecture?
Key reasons for adopting Multi-Bot Architecture include:
- Scalability: Handle large volumes of transactions efficiently.
- High Availability: Ensures uninterrupted processing even if some bots fail.
- Faster Processing: Parallel execution leads to quicker turnaround times.
- Load Balancing: Distributes tasks intelligently to avoid overburdening any single bot.
- Flexibility: Enables simultaneous automation of diverse processes.
- Resilience: Ensures minimal disruption in case of individual bot failures.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces operational costs by automating repetitive tasks at scale.
Types of Multi-Bot Architecture
1. Sequential Bot Execution
One bot completes a task and hands over task to another bot for the next set of steps either in one single application or across applications.
Example- During Customer onboarding one bot is tasked to update the CRM system and on completion of the task, hands over to another bot to perform KYC checks, on completion of these check and approval to open an account, the task is handed over to another bot to update the Core Banking system and CIF.
2. Parallel Bot Execution
In this case multiple bots can work on different parts of the process simultaneously, especially when parts of the processes don’t have interdependency, and this saves time owing to parallel execution.
Example- During high load conditions, multiple bots can be invoked to execute invoice processing in parallel especially end of month type situations.
Example- In complex processes like airline ticketing, processes are forked without interdependency and execute in parallel to complete a large process faster.
3. Hybrid Multi-Bot Model
This is a case of using both sequential and parallel architectures together in order to optimize very complex workflows. Usually an optimization study and interdependency needs to be done to device this model so that all underlying systems and processes execute as per design and is tolerant to delays / failures.
Example- Complex loan underwriting processes such as personal loan or mortgage application processing for quick decisioning can be implemented. This needs to be validated for specific markets as it involves a high degree of digitization in the process.
Advanced Concepts in Multi-Bot Architecture and important considerations
1. Bot Orchestration: Efficient task distribution to optimize performance.
2. Dynamic Scaling: Adding or removing bots as per workload requirements.
3. Fault Tolerance: Mechanisms to handle Bot failures without affecting the process.
4. Intelligent Load Balancing: Using AI/ML models to predict workload and adjust distribution.
5. Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring for proactive issue resolution.
6. Workflow Optimization: Automating complex workflows using modular bot components.
Architecture Overview of a typical Multi-Bot system
The following diagram illustrates the concept of Multi-Bot Architecture, where a Central Orchestrator manages multiple bots interacting with various target systems such as Databases, Web Applications, ERP Systems, and CRM Platforms.
The graphic in Figure 1 represents a typical multi-bot architecture deployment for a report generation process. The Dispatcher collates the data from various sources and pushes it into a queue. This queue is operating on a first in first out basis. Each bot picks up an item on the queue and executes the task. The performer is responsible for the performance of the overall process and ensures that the load is balanced for optimum performance. Each bot generates its output in this case its then consolidated to generate a single report. This is an example of parallel bot execution.
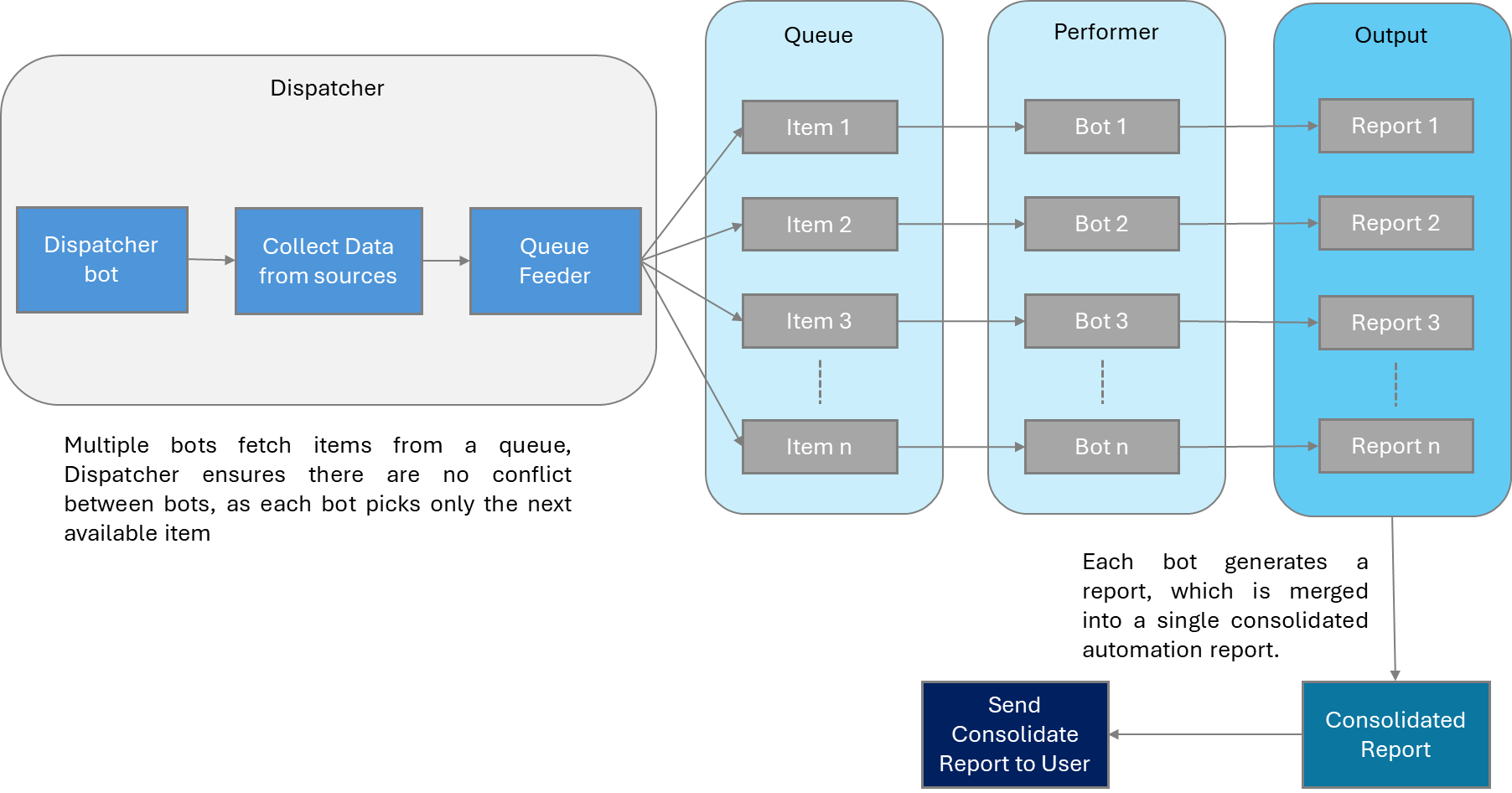
Figure 1: Depiction of a typical Multi-bot Architecture deployed for a report generation process
How Multi-Bot Architecture Works
- Task Initialization: User or system triggers automation.
- Queue Management: Tasks are placed in queues managed by the Orchestrator.
- Task Assignment: Bots pull tasks from the queue based on availability.
- Execution: Bots perform the assigned tasks, updating target systems.
- Monitoring: Orchestrator monitors execution and handles errors or exceptions.
- Reporting: Generate performance and audit reports.
Use Cases Across Industry Verticals
Manufacturing
1. Inventory Management: Bots monitor stock levels, place orders, and generate reports.
2. Supply Chain Automation: Automate vendor communications, order tracking, and invoice processing.
3. Quality Checks: Bots analyse production data to detect anomalies.
Banking and Financial Services
1. Fraud Detection: Bots work simultaneously to analyse transactions for fraudulent activities.
2. Loan Processing: Distribute tasks like document verification, credit checks, and approval workflows among bots.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Automate KYC and AML checks at scale.
Healthcare
1. Claims Processing: Bots process insurance claims, validate documents, and interact with databases.
2. Patient Onboarding:Automate data entry and verification from patient forms to electronic health records (EHR).
3. Appointment Scheduling: Multiple bots handle patient appointment booking, reminders, and rescheduling.
Telecom
1. Customer Support: Bots handle thousands of service requests and complaints.
2. Billing: Automate bill generation, adjustments, and notifications.
3. Network Monitoring: Bots check system health and report issues in real-time.
Retail and E-commerce
1. Order Processing: Bots handle order placements, updates, and fulfillment.
2. Customer Feedback Analysis: Analyze feedback and reviews to improve products and services.
3. Inventory Synchronization: Update stock levels across multiple platforms.
Best Practices for Multi-Bot Architecture Implementation
1. Design for Scalability: Incorporate dynamic scaling to handle workload surges.
2. Implement Redundancy: Use backup bots for critical processes.
3. Prioritize Error Handling: Implement robust error management mechanisms.
4. Monitor Performance: Regularly assess bot performance and health metrics.
5. Keep Logs Centralized: Use a centralized logging system to track issues and performance.
6. DR and BCP : Consider business continuity scenarios while designing. Take into considerations various failure points.
Multi-Bot Architecture is transforming how industries approach automation. This architecture allows enterprises to to scale operations, enhance productivity, and ensure business continuity even during high-demand scenarios. As industries continue to digitize, embracing Multi-Bot Architecture will be pivotal in staying competitive and agile in a dynamic and global market.


